lng impacts
on communities and ecosystems
LNG expansion has adverse economic impacts on the livelihoods of communities
Human rights and environmental justice concerns in LNG development

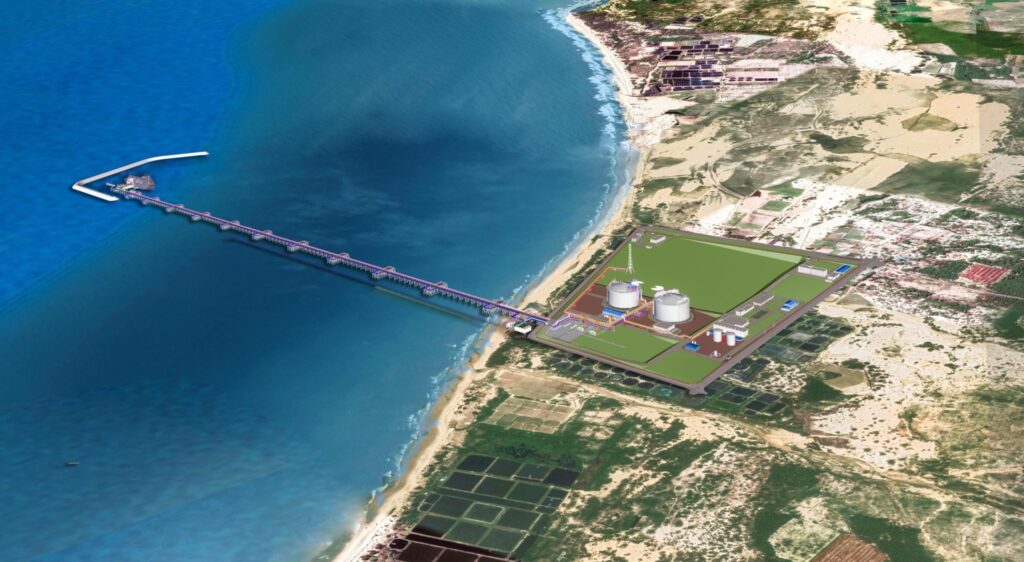
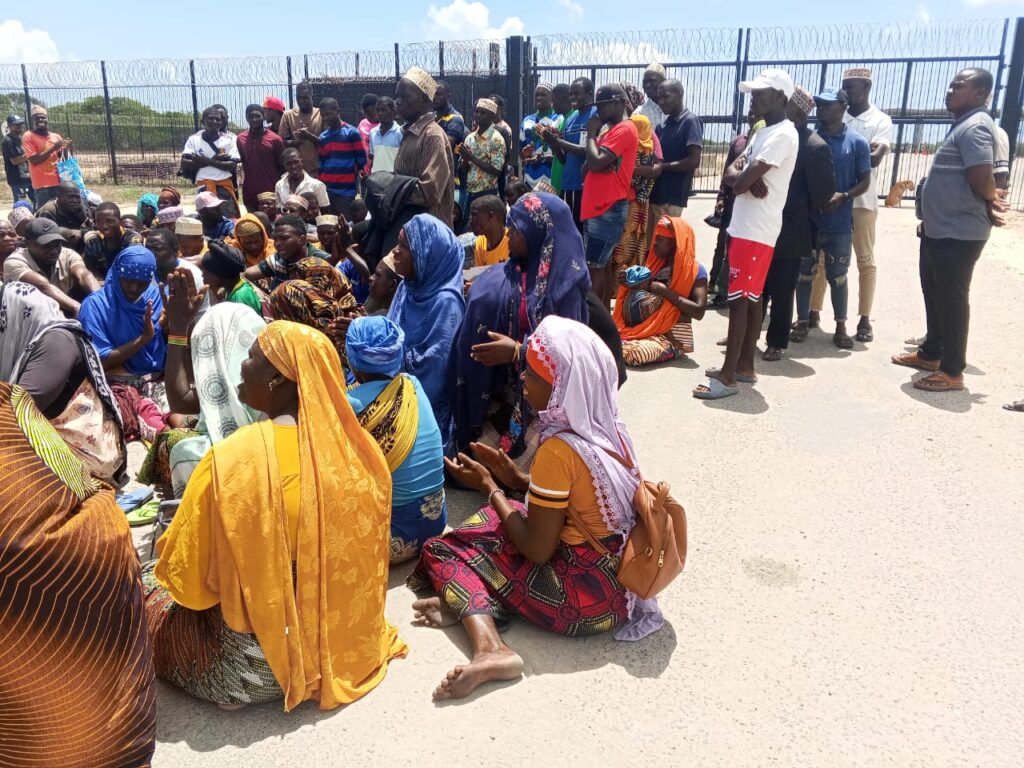
The rights of communities, including Indigenous communities, are often overlooked or violated in the development of LNG projects. For instance, TotalEnergies’ Papua LNG project in Papua New Guinea — currently under development (see the case study below for more informations) — reportedly failed to provide nearby communities with clear, accessible information about project risks in their first languages. Additionally, the Indigenous Peoples potentially affected by the project do not appear to have been adequately informed and consulted — denying their rights to Free, Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC).
Similar violations have been reported in the US. For example, the Rio Grande LNG project by NextDecade has been criticized for failing to obtain FPIC from the Carrizo/Comecrudo Tribe of Texas, who were neither consulted nor gave their consent to the project.
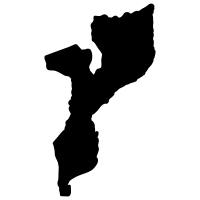
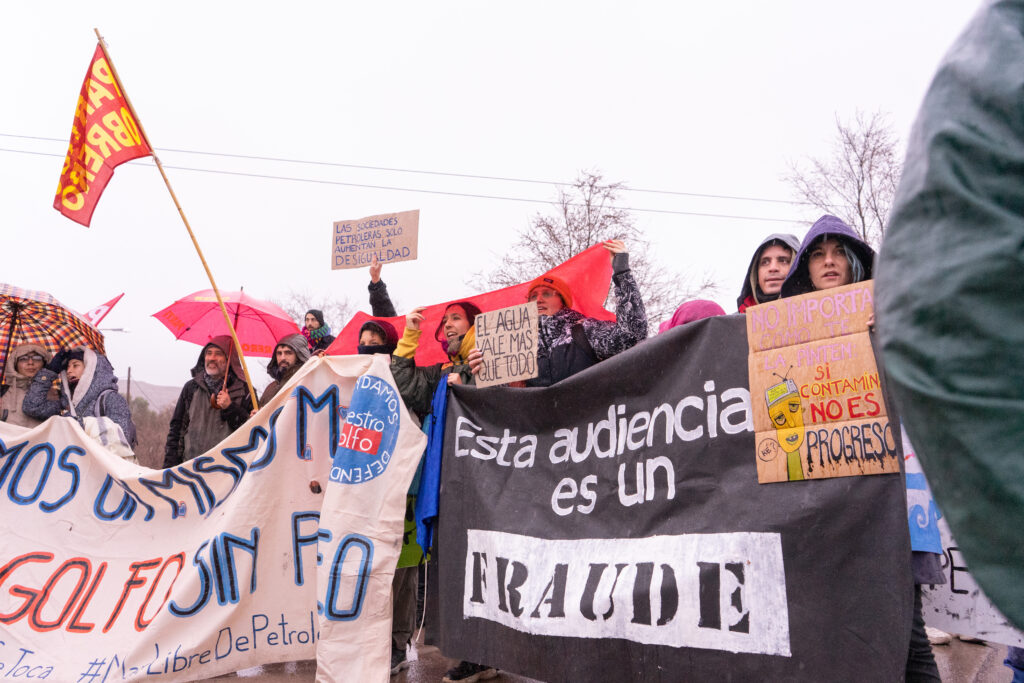
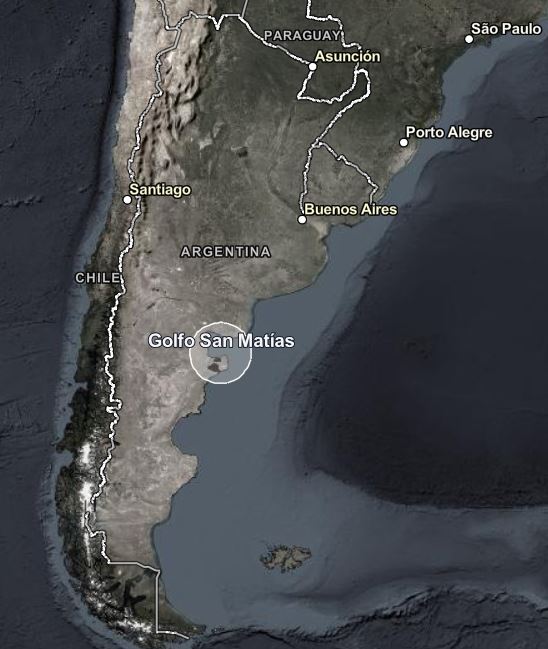
LNG projects developed in conflict-affected regions are also associated with serious human rights violations, in some cases leading to legal action. In Mozambique, a legal action has been initiated against TotalEnergies and its Mozambique LNG project, with journalistic investigations revealing serious human rights violations.
More broadly, the development of LNG terminals often raises concerns about discrimination and environmental racism. These projects frequently occur in areas with high poverty rates or in predominantly Indigenous or communities of color. In the US Gulf Coast, for instance, Louisiana has been labeled a « sacrifice zone » due to the concentration of oil refineries, petrochemical industries and more recently LNG terminals. The developments have had significant health and economic impacts on neighboring communities, which are largely Black and low-income.
Additionally, LNG terminals are sometimes developed in countries with authoritarian or non-democratic regimes, potentially strengthening those regimes while raising questions about the equitable distribution of LNG revenues and the ethics of supporting these types of governments. This concern has been echoed in criticisms of the European Union’s decision to shift its gas dependency from one authoritarian regime to another — moving reliance “from PutinGas to TrumpGas.”
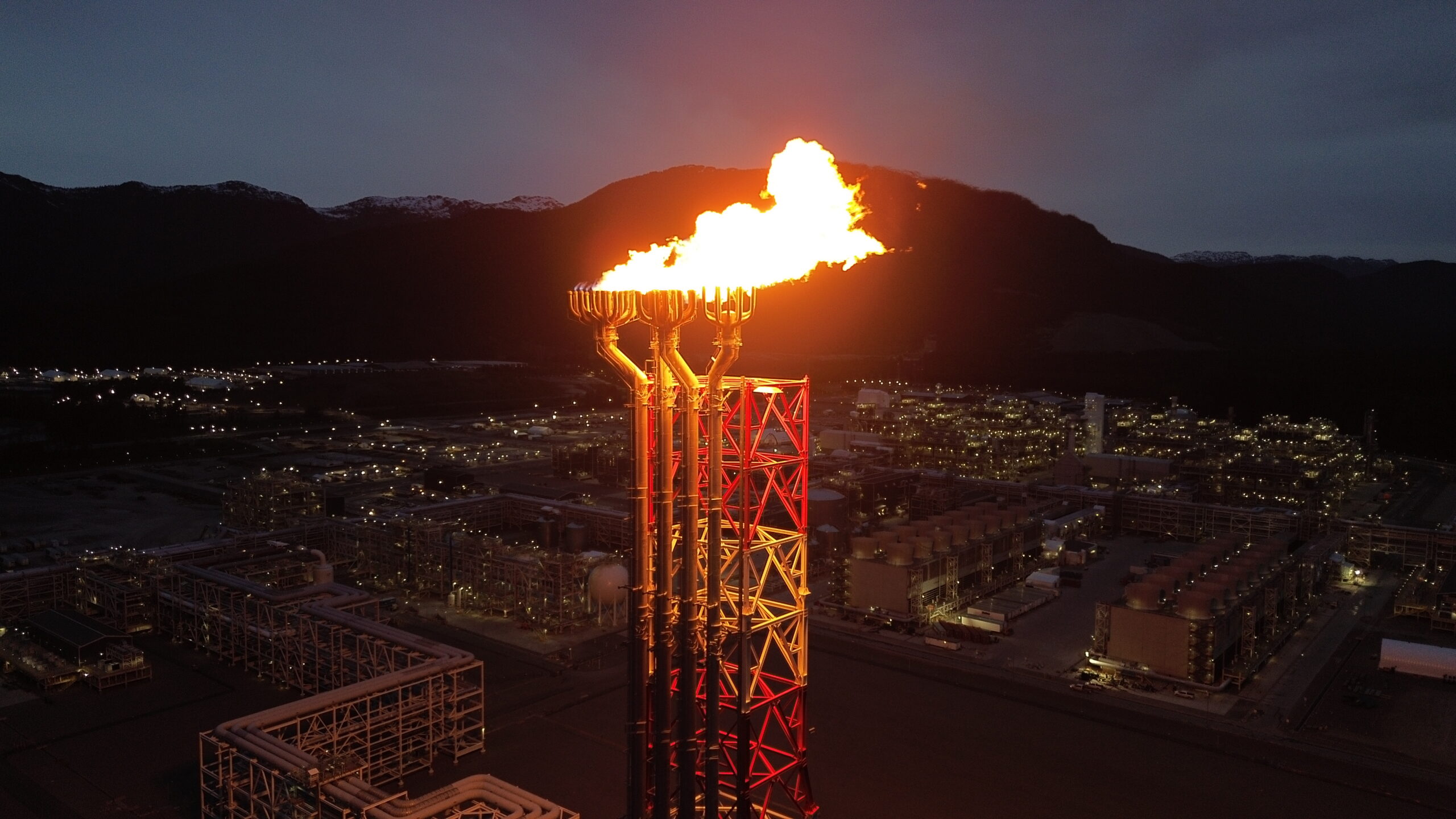
Pollution, premature death, and public health impacts across the LNG value chain
LNG expansion dramatically affects ecosystems and biodiversity
LNG infrastructure and methane carriers have a significant range of impacts on ecosystems. Commonly reported impacts include:
Case studies
We – NGOs fighting LNG expansion and communities affected by the LNG boom – call on banks to adopt comprehensive policies to end all financial services for new LNG projects, associated methane carriers, infrastructure, and LNG developers.
We call on insurers to stop providing coverage for new LNG export and import terminals.
We call on companies to immediately halt LNG expansion plans, which are having devastating impacts on communities, ecosystems, and the climate.